Contamination diagnosis and studies in pharmaceutical industry – an essential stage in decontamination process
Parole chiave: Contamination-Diagnosis-Studies-HVAC-API-toxic-heavy metals-decontamination
The diagnosis is the main point of decontamination works as it allows to focus on the real and effective problem and to target the contamination in every part of the processes. The team MSE*-Techno-One-Jobbing is completing a DIAGNOSIS before doing any works in order to optimize the operations with the highest safety level. It allows, among others, to design the decontamination works taking into account the history and the future of the client’s plant. The team is proposing turnkey cleaning and decontamination services comprising the diagnosis and the decontamination design and works, the overall being called Good site Decontamination Practices (GDP).
The team has performed several works the past years based on the GDP model. Among these works, two projects, representative of the team’s works will be described in the present case study:
- Decontamination and dismantling works at an oncological production unit of a top ten world’s largest pharmaceutical company plant: An oncological production unit belonging to a top ten pharmaceutical world producer had to be dismantled and redesigned (space reorganization and existing processes improving) in order to receive a new product. For this purpose some parts of the unit had to be eliminated and others to be reused. The unit was composed of several rooms (production areas, personnel and equipment airlocks…), equipment (formulation line with tank and mixer, filling machine, freeze dryer, sealing machine, semi-automatic inspection machine, washing machine and autoclave), central air treatment units and deduster units with associated networks. The team’s work consisted in first place to make a study so as to localize the contamination and to define the best decontamination solutions and validation technics.
- Decontamination of different surfaces soiled by heavy metals at a research laboratory: A research laboratory was confronted to three toxic heavy metals contamination (Mercury, Tellerium and Cadmium) which were used for the investigations and had to be removed. The work at the laboratory consisted in elaborating a decontamination procedure regarding the different types of surfaces of the premises.
The Good site Decontamination Practices methodology were applied in both cases. The GDP are in a general manner set up through three main steps:
- Diagnosis
- Works implementation
- Validation of decontamination
Diagnosis
The challenges of this study are numerous and permit to:
- check contamination nature, location and quantities
- target the areas to clean
- define the cleaning process
- define the molecules to track and the decontamination threshold to reach
- define the sampling and analytical technics
These different parameters differ from one process to another, and from one contaminant to another. For this reason the diagnosis must be systematically done before any work initiation.
1) The team makes first an EVALUATION ON DOCUMENTATION AND ON SITE INVESTIGATION so as to:
- identify the molecules to track and the decontamination level to reach
- put in place sampling and analytical methods
- make a sampling mapping
For the oncological production line, it appeared from site history (process documents, investigation with management teams and operators) that 7 different API were handled in this unit since 1970, which permitted in consequence to define trackers from literature (MSDS and API literature). Among these APIs, two trackers were chosen using their:
- toxicity level
- behavior to the cleaning process (solubility in different solvents, degradation in different medias)
- quantity handled in the unit
Then, the thresholds (decontamination level to reach) were defined using the worst case toxic molecule characteristics to calculate the allowable quantities of the contaminant by using the MACO (Maximum Allowable Carry Over: calculation based on the dose and/or toxicological data of the compounds).
Two different thresholds were defined keeping in mind the future of each part of the unit:
- parts to be reused: threshold defined to avoid cross-contamination with the new product
- parts to be dismantled: threshold defined to avoid workers and environment contamination
The lower threshold defined was of 1µg/25 cm² and was submitted to the client for approval before the start of the works.
Next, sampling and analytical methods were adopted and validated. These methods were validated ones from the client’s site: swab test and internal analysis. In other cases, if not existing, the sampling method (wipe test: kind of media and solvent, air sampling etc.) is validated by measuring the recovery rate of a known amount of the pure molecule to track.
Afterwards, a sampling mapping was defined using documentation (P&ID, isometric diagram), the procedures (Cleaning In place SOP, Standard Cleaning SOP, Maintenance procedures for HVAC) and on site investigations to select the worst places where the API could accumulate during site life. Other contaminants as well were looked for as asbestos and heavy metals in different facilities. At least 120 points have been chosen for the sampling mapping.
2) Secondly, a DECONTAMINATION SOP is defined with proposal of cleaning agents (surfactant or degradation agent) and performance qualification of their efficiency on different representative surfaces.
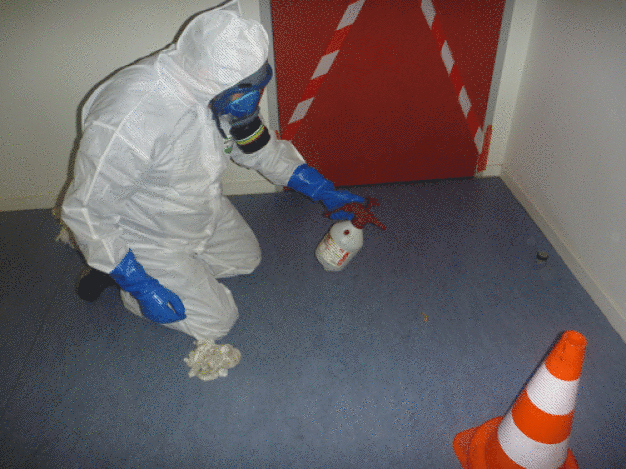
With regard to the research laboratory, this part of the study was aimed to define the best decontamination solution according to the different kind of surfaces. An evaluation of different decontamination solutions efficiencies according to the contaminant and the surfaces nature have been done. For this purpose, chemical dosage measurements have been compared before and after decontamination.
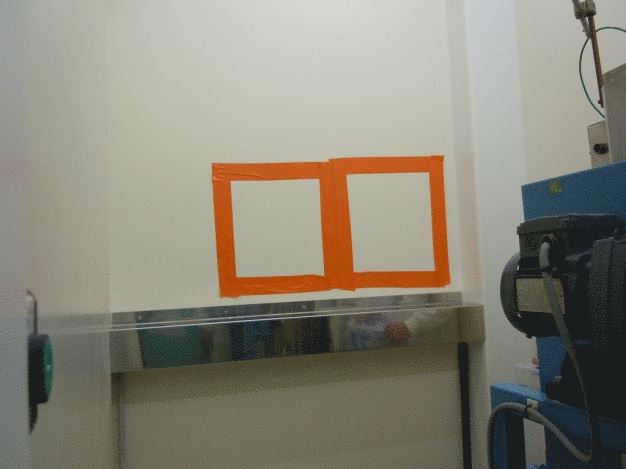
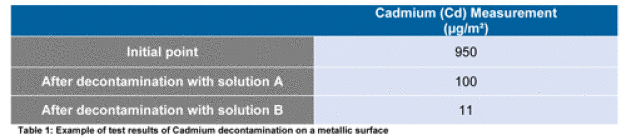
Tests have been performed on different kind of surfaces (stainless steel, painted surfaces, PVC) by applying onto same size areas two different decontamination solutions in order to compare their efficiencies (see Figure 1). Chemical dosage measures were done before and after the decontamination tests in order to determine which one was most efficient and which removed the best the contaminants.
As it is showed on table 1, the cleaning of a metallic surface with the solution A or B allows to decontaminate this kind of surface from cadmium contamination. However, the decontamination with the solution B permits to reach a threshold 10 times lower than with the solution A.
The tests performed on the other surfaces and on Mercury and Tellerium, have been as well successful with the decontamination solution B, which have been chosen for the decontamination works.
This complete diagnosis allowed us to define the procedure the team had to follow in order to remove the heavy metals from the different surfaces using the appropriate decontamination solution.
3) Finally, after the points above the DECONTAMINATION WORKS TO CARRY OUT are defined.
After cleaning agent selection, the intervention safety (LOTO procedure to implement, CPE to put in place and PPE to wear), the decontamination work and the decontamination performance qualification are established.
For the oncological production line, additionally to the sampling analysis (swab tests performed in the different chosen spots defined in the sampling mapping), were done Heat, Ventilation, Air Conditioning (HVAC) and extraction piping and ducts video inspections with a robot.
Analyzing both results (contamination mapping and video inspections showing quantities of API), the decontamination level to reach and the site constraints (utilities, production), the team suggested full technical specifications to realize site decontamination.
Works implementation
In a general manner, the decontamination works are always done starting from the top (roof) and going down to the rooms (ceiling, walls, equipment and floor). All the personnel is equipped with different Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): protective suit, overboots, air-filtration system with panoramic hood and gloves. Nevertheless, in order to protect the environment (rooms and surrounding areas of the working zone), Collective Protective Equipment (CPE) are put in place as confinement structures with depressurised unit (air-suction with HEPA filter) and glove-bags (to confine in a sealed way smaller areas such as ducts and holes). The confinement structure is put in front of the unit or room to decontaminate so as to allow the operators to decontaminate the equipment and remove PPEs in a safe manner while exiting the unit after works.
At the oncological unit plant, based on diagnosis and the future of every part of the unit, the whole works have been performed by the team MSE-Techno-One-Jobbing starting from the project management with the client, going through decontamination and dismantling works and finishing with decontamination validation and provision to the client of a contaminant-free unit ready to receive a new product in time.
As regards to the research laboratory, periodic decontamination works are now performed based on the initial studies done by the team.
Validation of decontamination
In order to control the decontamination process, different validation methods can be used:
- Wipe tests with ICP MS analysis: wipe tests are performed by swabs on surfaces to quantify the contaminant
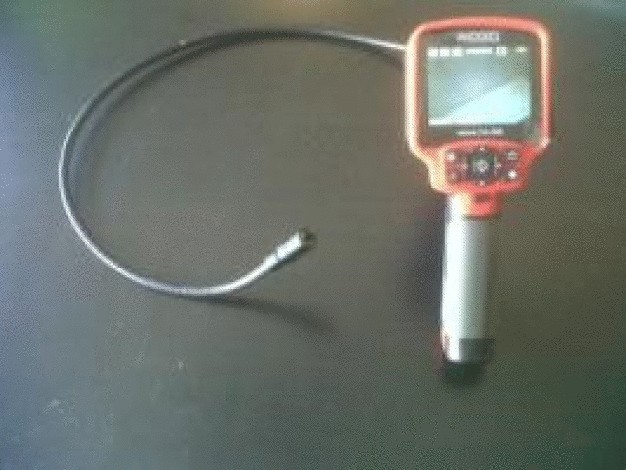
- Endoscopy for visual inspection of HVAC and deduster ductwork: The correct decontamination of the ducts is controlled by endoscopy. Nevertheless, in order to validate the decontamination in some parts of very contaminated ducts, a swab test can be done.
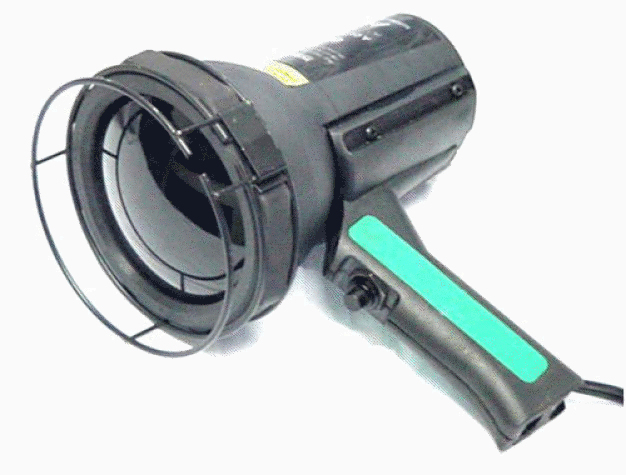
- UV light for visual inspection when the contaminant contains an aromatic cycle
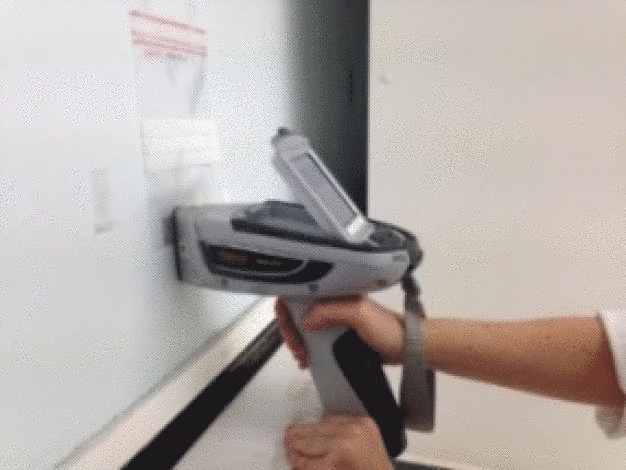
- X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer for surface analysis: It is used for example to measure mercury (Hg) content
For the works at oncological production line, three sampling mappings have been done in relation with the progress of the works inside of the rooms, equipment, HVAC units, dedusters and some very contaminated ducts (revealed during diagnosis) by swab testing. The threshold has been reached in every part of the unit.
The equipment, rooms, HVAC and dedusters to be reused were ready after the works to receive the new product, while the HVAC units and ducts to be removed have been dismantled by the team after decontamination works.
These case studies show how important the diagnosis phase is in order to prepare the works to be performed and to deal with every contamination in different configurations on a case by case basis. By the GDP appliance, decontamination works can be performed at any plant, unit, process, equipment to be decontaminated in order to be re-used, transferred, dismantled, sold, eliminated as waste,… and for every contaminant (toxic, corrosive, explosive, CMR, …) representing an obstacle to a healthy environment for the operators and the production.
CURIUM
69700 Montagny
France